Baidu Faces Consecutive Declines Amid Stiff Competition in AI and Internet Markets
Baidu Inc., a leading player in the Chinese technology sector, has reported its third consecutive decline in quarterly income, prompting concerns regarding its internet research and artificial intelligence (AI) initiatives, which are struggling under intense competition. The significant challenges facing the company have raised eyebrows among investors and industry analysts as Baidu attempts to navigate a transforming market landscape.
For the quarter ending in December, Baidu’s revenues fell by 2%, totaling 34.1 billion yuan (approximately $4.7 billion). This figure, while exceeding the average estimate of 33.4 billion yuan, still signals a troubling trend for the company, particularly considering a staggering 29% drop in operating income. The market response was negative, with Baidu’s shares declining over 7% in New York.
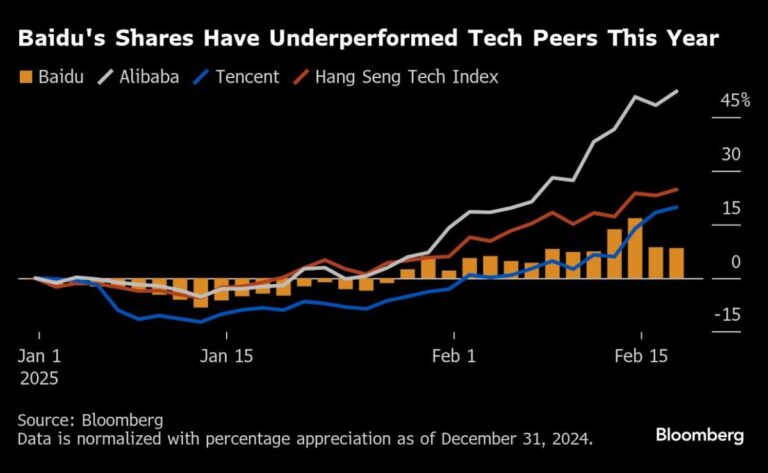
The broader context for Baidu includes a wave of financial results from other major tech players in China, which have attracted significant attention from investors. Notably, the Hangzhou Deepseek startup recently caught the eye of Silicon Valley by releasing AI models capable of competing with or exceeding those from Western counterparts, contributing to a rising tide of market optimism for companies like Tencent Holdings Ltd. and Alibaba Group Holding Ltd. Unfortunately for Baidu, this momentum largely passed it by, highlighting its struggles to maintain competitive parity in the rapidly evolving tech arena.
In the company’s December quarter, a notable bright spot emerged: income from generative AI saw a noteworthy increase of 26%, a rate faster than previous quarters. This jump was primarily driven by services catering to startups and developers seeking computing power. Nevertheless, this growth was overshadowed by deteriorating profit margins and other indicators of weakness in Baidu’s core operations, raising further questions about its overall health.
Baidu’s advertising revenue has suffered as it loses market share to social applications such as Douyin, Xiaohongshu, and others powered by ByteDance Ltd. The economic slowdown has compounded these challenges, making it difficult for Baidu to reverse its fortunes. Meanwhile, Deepseek’s recent advancements using open-source models and minimal training costs threaten Baidu’s own approach and market position in AI technologies.
In a surprising move last week, Baidu also adapted its models by integrating the new R1 model developed by Deepseek into its flagship chatbot, a strategic decision aimed at responding to competitive threats. Historically, Baidu has been a pioneer among Chinese technology firms in deploying large language models and was one of the first to promote its own chatbot, Ernie, with a monthly subscription fee of $8. However, in a bid to attract users, the company recently reversed its pricing strategy, now offering the service for free.
According to Bloomberg Intelligence, Baidu’s financial results reveal the scale of the challenges it faces, with adjusted operating profit shrinking 29% year-on-year to around $5 billion, largely attributable to a significant 7% decline in its core advertising sales. Furthermore, Baidu’s overall profit margins dipped by 400 basis points, pressured by an increase in cloud AI sales that did not adequately compensate for the weakening advertising segment. Despite these hurdles, Baidu has found some positive traction in its Cloud AI operations, although the lower margins in that segment raise additional concerns.
Looking ahead, Baidu’s prospects appear increasingly tenuous. Recent strategic decisions, such as making its foundational models open source and halting monetization efforts for its Ernie Bot, are expected to exacerbate the ongoing challenges in a fiercely competitive market. Analysts anticipate that Baidu’s search engine will likely remain under continuous pressure throughout the year.
Despite these significant challenges, Baidu still boasts some inherent advantages in the Chinese AI landscape. The company is collaborating with Apple Inc. to develop AI-driven features, particularly for the iPhone’s AI system in China, as reported by Bloomberg News. However, the pressure of ensuring content censorship falls more heavily on Alibaba, which is gearing up for a mid-year launch of its own initiatives.
During a recent earnings call, executives emphasized Baidu’s commitment to advancing applications for potential future use cases. "While AI chatbots are a vital, albeit nascent phase in the development of AI applications, a true ‘killer application’ has not yet emerged," Junjie, the financial director, remarked to analysts. "Our focus is on maintaining a rapid and determined pace in transforming AI technology by identifying what users genuinely need and want for the next generation of searches."
Significantly, Baidu founder Robin Li’s absence from a high-profile meeting with Chinese President Xi Jinping has drawn scrutiny, particularly as prominent figures like Jack Ma and leaders from emerging startups were present. This raises questions about whether Baidu is falling out of favor with Beijing, which relies on the private sector to revive the second-largest economy. Nonetheless, Li participated in the earnings call to discuss Baidu’s AI initiatives, including developments in robotaxi technology and research.
As Baidu strives to regain its footing in the highly competitive tech landscape, the coming months will be critical in determining whether it can redefine its strategies and overcome the numerous hurdles it currently faces.